Creating things with 3D printing is undoubtedly thrilling and fulfilling. This is because the end product is always useful and beautiful to behold. When it comes to 3D printing, there are limitless possibilities, especially when you use PLA filament.
The properties of PLA make it ideal for the production of bottles, plastic film, and biodegradable medical devices like pins, screws, rods, and plates designated to biodegrade in 6 – 12 months. Additionally, its ease of melting makes it an excellent fit for 3D printing applications.
So, if you decide to use PLA filament to create 3D objects, you will be making a great choice. However, this also leads to the question: Is it safe to use PLA to create kitchen utensils like printed food storage boxes or drinking cups for beverages and food? The simple answer is Yes, PLA is food safe. However, it isn’t ideal for long-term storage. You will discover why and learn more about PLA in this well-detailed article.
Polylactic Acid, popularly referred to as, PLA is a thermoplastic monomer Trusted Source Monomer - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The monomer is a halogenated norbornene prepared via Diels and Alder cycloaddition between a halogenated olefin, for example, 2,3-dichlorohexafluorobut-2-ene, CF3(Cl)C=C(Cl)CF3, and cyclopentadiene. www.sciencedirect.com gotten from organic, renewable sources like sugar cane, corn starch, tapioca, and potatoes. It is an incredible 3D printing material. Little wonder why it is the go-to option for users across the globe who need top-notch 3D prints.
Furthermore, PLA is a thermoplastic aliphatic polyester Trusted Source Aliphatic Polyester - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The aliphatic polyester (b) is PLA consisting of l-lactic acid and/or d-lactic acid units. www.sciencedirect.com and is one of the most preferred materials for manufacturing additives. Similar to most 3D printing materials, PLA filament has its pros and cons.
PLA is completely compostable and releases a remarkably reduced number of harmful fumes when burned up.
Composting PLA is specialized and requires a controlled atmosphere. This requires further financial investment.
As the name suggests, food-safe means that a food-grade material is also ideal for its designated purpose — that is, preparation, handling, and storage of food— without leading to any harm.
Certain terms are associated with food safety — and it’s only right that you know them. Luckily, we have these terms explained below. Take a look!
Food quality isn’t referred to solely as a product property because there’s more to it. Instead, it is viewed as a representation of the whole characteristic properties of a food product. This revolves around the harmlessness of food to human health, as it serves primarily as our source of nutrition.
Food contact surfaces include every surface made up of toxic materials built to resist the environment of their designated use. It also involves the impact of disinfectants, cleaning agents, and other cleaning procedures.
Particles can easily be transferred from one material to another once they make contact. For instance, the parts of the 3D printer make contact with the 3D printed object, and the 3D printed object touches the food.
This occasional contact has an extremely low migration rate. In this case, the classification of food mainly refers to objects that make contact with food for a long time, like plates, utensils, food forms, and straws.
In other words, a material can be classified as “food-safe” if you can use it to prepare, handle, and store food without any food safety concerns. It is worth noting that food-safe materials do not affect the smell or taste of food.
Before a material can be recommended as food-safe, it must meet these criteria:
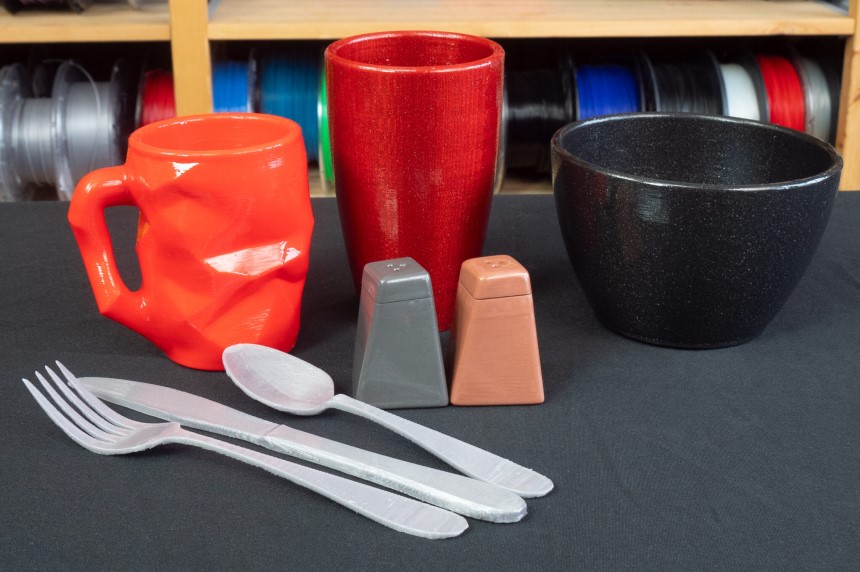

Irrespective of your plans, it is essential that every material you use for your food is 100% safe. This helps you to maintain your health and prevents your food from becoming useless.
3D printing also comes in handy in the medical field, especially in situations when there’s a need for materials that are biocompatible, harmless, and safe to the body of humans.
Over the years, 3D prints have become extremely popular. They are now used in many industries worldwide, as they offer excellent solutions for both personal belongings and food containers with a unique touch and amazing design work.
If you are making plans to print a 3D object that will come in contact with food, the last thing you want is bacteria growth. Preventing bacteria from growing on your 3D object helps you to eliminate any possible contamination for you or others around you.
Here’s the thing, when your 3D printed parts make contact with surfaces already infested with bacteria, it increases the chances of bacteria growth. Since PLA is organic and porous, it may have small cracks not visible to the human eye.
The presence of these cracks encourages germs and bacteria. If this happens and your 3D print is not cleaned carefully, they will flourish and keep multiplying. So, what can you do to prevent the growth of bacteria? All you need is a smooth material that would hinder food from getting stuck in your 3D object.
It is highly recommended that you use PLA only for kitchenware applications and disposable cutlery. Additionally, you should also steer clear of PLA if you intend to store raw meat or egg, as they are more liable to harm-causing bacteria.
PLA is made from organic materials, making it biodegradable and conclusively safe for food. However, some manufacturers mix varying degrees of non-organic additives with their PLA filament to modify features such as smell, color, strength, and a few others.
For this reason, you need to carefully choose the materials and technologies you use in the production of 3D printed objects. Note that 3D printers also release a few ultrafine particles that can cause health hazards. You can prevent this from occurring at the washing and finishing stages. Additionally, there is a possibility that your 3D print model might have hot ends containing harmful chemicals.
This implies that there’s a slim chance that tiny particles might mix with your PLA even if you use a safe PLA filament. Regarding this, you should ensure that you use stainless nozzles. Make sure you always clean your nozzle when printing food-safe objects.
Certain materials used in the production of 3D objects contain harmful chemicals. This is particularly accurate for filaments like ABS, making it an unsafe option to consider for food. ABS is known for having a large amount of ultra-fine particles, which can cause health challenges in humans when ingested. You should not use ABS for the production of your kitchen utensils.

Over the years, PLA has undergone many tests under separate conditions to determine its level of food safety. These tests were conducted at different temperatures. Besides that, the contact time between the ingredients frequently found in food and the printed material was also taken into account. Lactic Acid is a common and essential food ingredient that can be found in breast milk. Research shows that the number of individuals that absorb lactic Acid via PLA is around 700 times lesser than the intake of Lactic Acid by breastfed infants.
If PLA is colored, it means one thing — there has been an introduction of additives into the mix. These additives are solely responsible for the PLA color and strength optimization. Therefore, if you desire to print 3D models or objects that make contact with your food, you should opt for the untreated and natural PLA as your go-to material for printing.

Even if your PLA filament is safe for food, there is still a slim possibility of contamination from the hot end of your 3D printer. According to experts’ reviews, a PLA filament must be durable and flexible. Hatchbox PLA 3D fits the bill, thanks to its high-quality composition.
The processing and printing of PLA involve a powerful combination of heat and chemicals, which is harmful to human health. The only exception to this is hot ends with nozzles made of stainless steel.
Generally, every desktop 3D printer with ABS or PLA emits a great deal of ultra-fine particles that can be found on your printed model. Inhaling or swallowing these ultra-fine particles is harmful to your health. While ABS can easily be classified as the most harmful 3D printing material, printing 3D objects can be performed in a room with adequate ventilation.
Also, ensure you do not eat close to your 3D printer to prevent your food from getting contaminated by particles during the process of printing. Based on customer reviews, a 3D filament dry box should be able to accommodate the needs of various filaments. EIBOS Filament Dryer is an excellent fit, as its adjustable heat temperature feature is ideal for any filament.
Every model or object produced via 3D printing has pores that look like cracks. This makes it the perfect breeding ground for bacteria and germs. Unfortunately, models printed with PLA are not excepted. Immediately the germs and moisture settle in these cracks or pores, it becomes almost impossible to get rid of them completely.
The primary reason this happens is that PLA is not dishwasher-safe, which means that it can easily warp or melt when placed under high temperatures. Circumstances like this lead to the assumption that PLA is only safe for single use. When used repeatedly, it can become harmful to human health if some safety measures are not put in place.
For instance, if your 3D objects are printed for one use, you need not worry about bacteria growth. However, if you decide to repeatedly use the object (cup or plate), you need to ensure that you take special care.
Also, it is not advisable to bring your 3D printed object close to your eggs or raw meat, as they are more prone to toxic bacterial growth. Indeed, PLA is not dishwasher-safe; nonetheless, it can still be washed using mild antibacterial detergent and lukewarm water. This lessens the risk of molten prints and eliminates every surface bacteria.
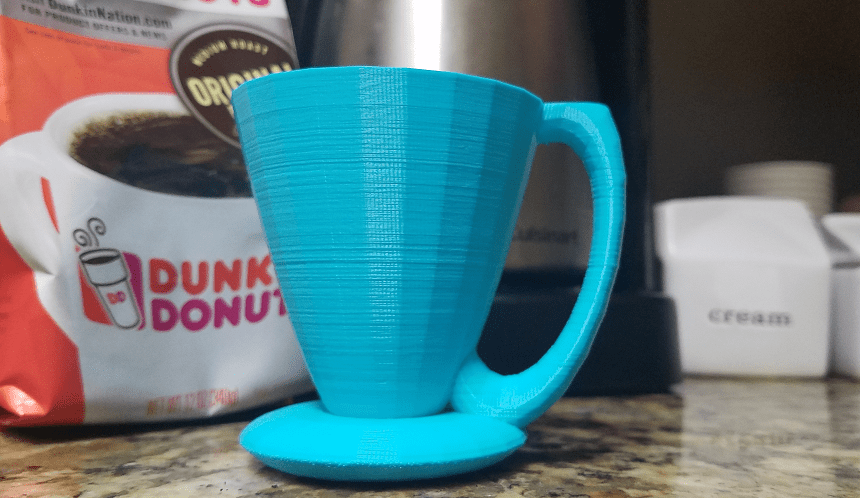

PLA is biodegradable, thanks to its natural origin. This is why it is an excellent option to consider for printing food-safe kitchenwares like bowls, plates, shot glasses, pet food dishes, and coffee mugs. Under suitable conditions, signs of biodegradation in PLA will begin to show. PLA decomposes best in a high-temperature environment with the presence of several microorganisms.
Besides their biodegradable characteristic, PLA is also compostable, as they serve as a food source for microorganisms. Once there is a temperature of about 60°c, moisture, and microorganisms, the biological decomposition of PLA will happen. Conversely, when placed under normal pressure and room temperature, PLA takes many years to decompose.
It is worth mentioning that the presence of direct sunlight alone does not accelerate the decomposition process. Instead, it causes the material to become pale or lose its color. This is because ultraviolet light is irrelevant without a corresponding source of heat.
Without a doubt, 3D printed objects are easy on the eye, particularly when you use PLA filament. In times past, many individuals who wanted to use PLA to print their kitchen utensils have asked this question: Is PLA food safe?
If you were also wondering if PLA is safe for food, you should already know the answer, as we have provided you with the right answer in this comprehensive article and also went further to explain why and provide with you other vital PLA- related information.
Now, it’s up to you to use the details we have shared with you to your advantage. Always remember to check if the PLA filament is food-safe before using it for your kitchen utensils.