How to properly store filament is a significant issue for 3D printing hobbyists. Humidity and dust are the most challenging storage conditions for the most widely used filament materials, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and TPU.
Most 3D printing materials are hygroscopic, which means they absorb water molecules instead of repelling them. The filaments used in 3D printing are made from polymers, and when they absorb water, they can be broken down through hydrolysis.
The polymer in the filaments breaks down when heated at the point of extrusion, weakening the filament. Through repeated exposure, even what we consider relatively low ambient humidity can harm a filament. Keep reading for details on several ways to keep your filament safe and organized.

Any items printed using filament that has absorbed moisture (wet filament) won’t seem as neat or clean-cut as you want them to. 3D printing Trusted Source What is 3D printing? How does a 3D printer work? Learn 3D printing Learn how to 3D print. 3D printing or additive manufacturing is a process of making three dimensional solid objects from a digital file. 3dprinting.com is disrupted when using wet filaments because moisture in the thermoplastic evaporates when it is heated. As a result, the material’s composition contains air bubbles, leading to stringing and 3D-printed components with poor print quality and strength.
For proper extrusion with wet filament, a higher temperature is required. When filaments made of materials like nylon, polycarbonate, and copolyester are heated and wet, hydrolysis is likely to occur. Hydrolysis is when the water the filament absorbed from the surrounding environment disrupts the polymer chains inside the thermoplastic. You will observe poor layer adhesion when using wet filaments. Swollen PLA filament can damage your 3D printer, clogging the hot end and potentially necessitating a replacement.
When storing a filament, the type of material does not matter as most filaments are hygroscopic, some more than others. The amount of moisture that each type of filament absorbs varies, and the best ABS filaments absorb less moisture as a proportion of weight compared to other polymers. Other plastics, such as Acrylic, PETG, Nylon, Polycarbonate, and Nylon Blends, absorb moisture more significantly and require storage with extreme care.
It’s best to store every type of filament properly and keep them in a dry environment and prevent dust and particles from settling on them. You can simply protect the filament from the way of airborne particles and moisture by keeping it in closed containers or other places.
There are several methods for effective 3D printer filament storage Trusted Source Filament Storage For 3D Printing: Your How-To Guide - 3D Printing Correct filament storage is vital if you want to get the most out of your 3dPrinting filament. Click here for a filament storage how-to guide 3dprinting.com , and some methods are either costly or time-consuming. The following are the best ways to store filament so that it doesn’t come into contact with moist air and dust:
The following are various types of boxes and containers in which you can store your 3D filament spools:
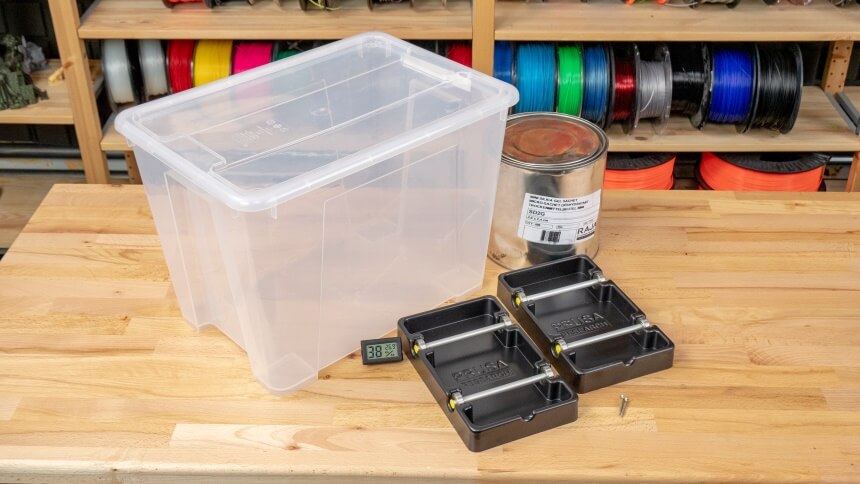

You should try to find something large enough to stack a few spools at least 20 cm in diameter, and the height should be roughly 40 cm, depending on how many filament spools you intend to stack. Desiccants are necessary for storing the best PLA filaments in containers and storage boxes. A desiccant is a hygroscopic substance that selectively absorbs all of the ambient moisture in an area. Desiccants can be bought as beads but are typically found in tiny bags.
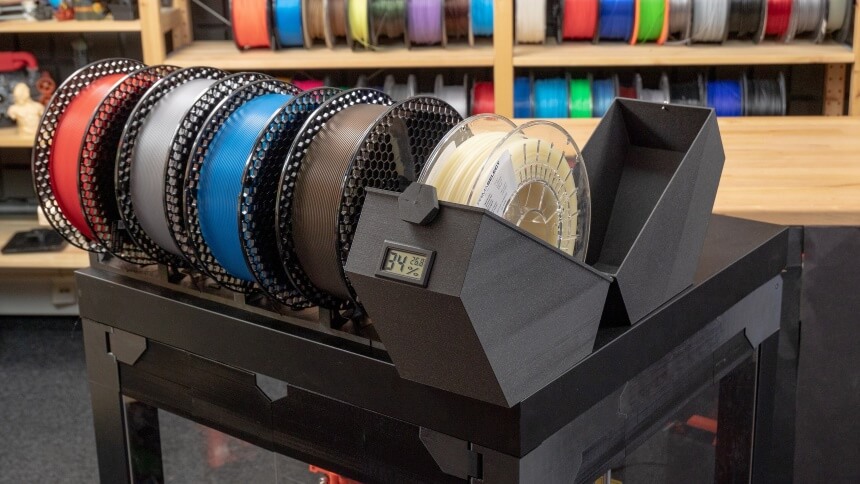
The multipurpose dryer stations feature moveable shelves, a 3D printer station, and storage and dryer for 3D printer filament. Before purchasing, ensure the filament dryer box is big and sturdy enough to store your filament.
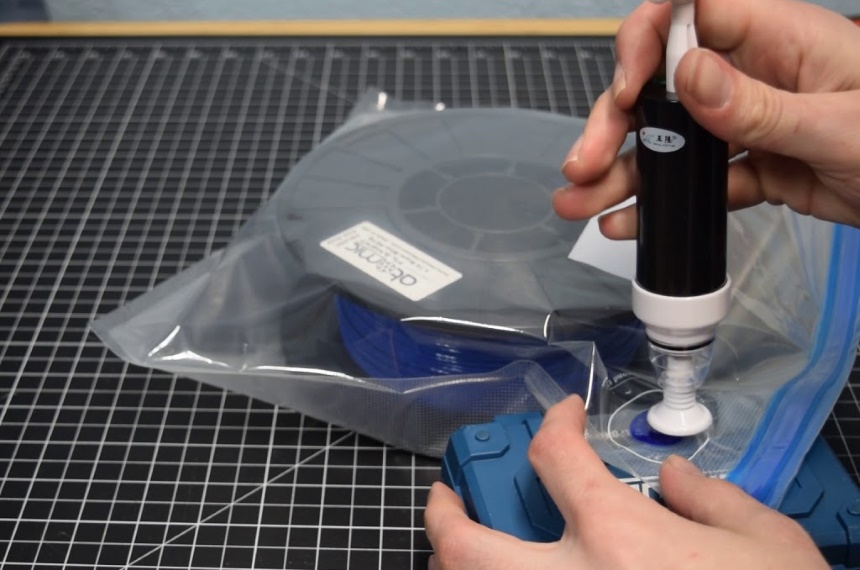

To make the most of your space, you should be able to fit three 1-kg spools in each. Vacuum bags inevitably contain some moisture after being sealed. Although it’s not necessary, add some desiccant to ensure you get rid of any remaining moisture before sucking out all the air.
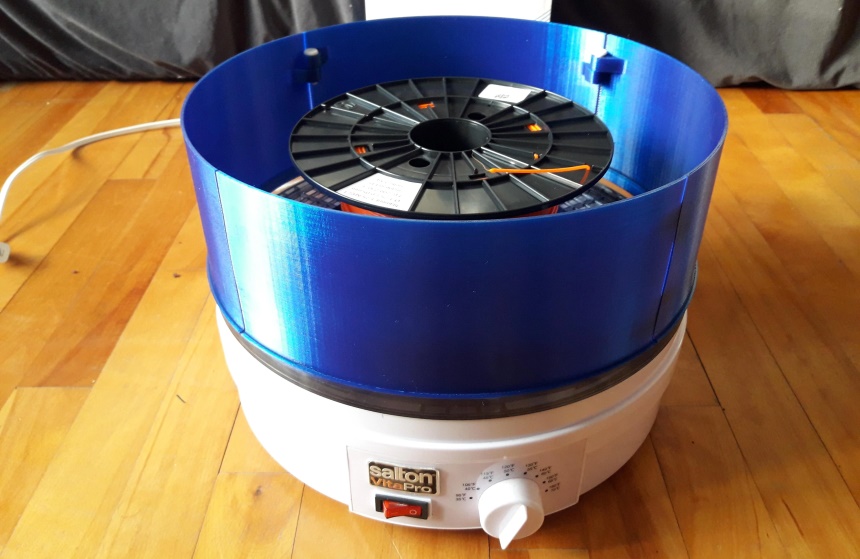

Most filament dryers operate by storing the filament in a gently heated space where any moisture can be evaporated. Additional features offered by purchase-only dryers include a timer, display, temperature controls, or fan.
Just keep a watch on your power bill since using an electrical device to store your filament may prove to be an expensive option in the long run. If you wish to build your filament dryer, you can find some excellent project designs online, with free download files and a video to follow.
Although we refer to it as wet filament, it is not always easy to tell if a filament is affected by moisture in 3D printing by simply touching it. When you are 3D printing, sizzling sounds from your printer and bubbles appearing in the filament as it is heated are signs that your filament has absorbed moisture.
Other signs of a wet filament include stringing, blobbing, and poor layer adhesion in the 3D-printed part. Before the print process, it can be challenging to determine whether the filament has absorbed too much moisture. However, if you discover that your filament spool is less flexible than it used to be, that may indicate that it is moist.
Drying the filament is an essential step in the 3D printing process as it greatly increases the likelihood of a successful print product. The following are ways to ensure your filament is free from moisture:
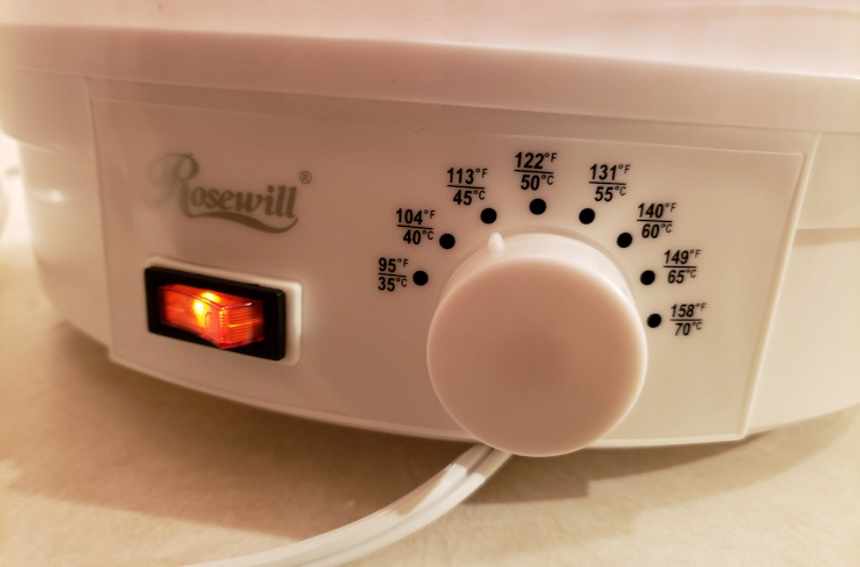

|
Material |
Temperature |
Drying time |
|
PETG |
65°C |
3 hours |
|
PC |
75°C |
6 hours |
|
PLA |
55°C |
3 hours |
|
ASA |
65°C |
4 hours |
|
ABS |
65°C |
3 hours |
|
TPU |
55°C |
4 hours |
|
Nylon (PA) |
75°C |
12 hours |
The simplest filament dryers comprise a heated container that can fit at least one filament spool. More advanced machines include extra features like spool rotation and ventilation for consistent heat distribution.
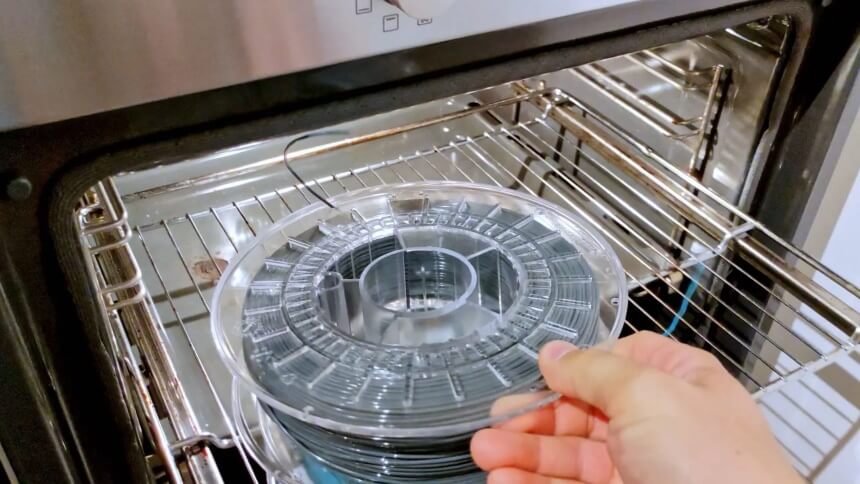

There are particular temperatures for various filaments. Hobbyists must also take the material of the spool holder into account because you don’t want it to melt or burn in your oven.
It’s also a good idea to understand how precisely your oven can maintain the temperatures mentioned above. You risk melting all the plastic and fusing your entire spool if the temperature deviates too far from the desired temperature. The best 3D filament for outdoor use, particularly ABS, can emit unpleasant scents and fumes, which is not what you want in a food-preparation device. After your filament has finished drying, give your oven some time for ventilation.
Most 3D printing plastics Trusted Source The Plastics of 3D Printing | Tools, Publications & Resources By Jason Griffey | Editor’s Note: This is the third of a series of posts excerpted from Jason Griffey’s Library Technology Report “3D Printers for Libraries.” The substrate for FDM printers are almost exclusively some form of thermoplastic that is delivered in an extruded wire-like form on a spool. It is usually called “filament” in the generic. www.ala.org contain heat-sensitive compounds that can be eliminated by periodically drying the filament in an oven or dryer. This can reduce the strength and quality of printed parts, and the material would become more brittle and of worse quality if it were overdried. Using suitable storage techniques can stop your filament from absorbing moisture in the first place, and you shouldn’t overdry it either.
Storage of filaments is a crucial component of 3D printing. Whether you decide to make your own DIY filament dry box or buy one, it’s essential to keep your 3D printer materials dry. If you don’t take the proper precautions, your filaments can get wet and no longer be usable, leading to substandard prints and wasted money.
Proper filament storage not only helps keep your filament tidy and dust-free, but it can also aid in preserving the quality of future prints. You can save time and money by trying to dry and store your 3D printing filaments properly.
Dry filaments perform best, promoting a fluid 3D printing process and high-quality prints with no or little stringing and strong layer adhesion. To safeguard your 3D printing materials and get the most out of your 3D printer, adhere to the above guide on how to store filament.