As 3D applications continue to increase, so do the variety of materials that are compatible to cater to different printing needs. In this guide, we will compare 3D printer resin vs filament, two of the most popular materials available in the market.
Some of the factors we evaluated are their respective precision, printing speed, adhesion, costs, ease of use, color options, and compatible materials. Besides that, we considered their application areas to determine the ideal materials for specific tasks and objects. We are confident that you will find our article on 3D printer resin vs filament a resourceful guide that will enable you to make an informed decision that will meet your needs.
FDM refers to Fused Deposition Modeling, and is the most popular form of 3D printing that is available today. It is also referred to as Fused Filament Fabrication. During FDM, a strand of thermoplastic material is heated at high temperature Trusted Source Safety Standards Aim to Rein in 3-D Printer Emissions www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov and extruded, and the melted filament is then deposited layer by layer starting from the bottom and moving upwards to print a 3D object. The resultant object, which may feature nylon or carbon fibers, has high heat resistance and mechanical strength which is ideal for making moving parts.
This technology was first applied in the 1980s. It is applied in development of new products, operational prototypes and manufacturing of end products such as plastic gears, cosplay helmets and LEGO, making FDM printers a useful tool for home users, manufacturers and mechanical engineers.
Pros
Cons
SLA refers to Stereolithography Apparatus which is the oldest type of 3D printing. It uses an additive method similar to FDM, but the materials and layering method are different. Instead of melted filament, SLA uses a curable photopolymer or liquid resin which is hardened to the desired pattern by focusing UV light on it in a process called curing. The layering differs from FDM because in SLA, the layers are placed on the platform from top to bottom to raise the model upwards out of the pooled resin.
SLA printing utilizes laser as a light source to draw each layer, and there are inexpensive 3D printers which use LCD to project the image into the resin. There is a form of SLA known as Digital Light Processing (DLP) which is often featured in home theatre projectors. This type of 3D printing uses a digital projector as a light source to place a two-dimensional layer or an entire slice of the object into the resin pool.
Objects printed by SLA printers have extremely fine detail and smooth surfaces.
Pros
Cons
In this section, we compare how long it takes to 3D print when using a SLA 3D printer vs FDM printer. We also analyze how the two types of printing differ in quality, materials, cost, precision and ease of use, among other key features.
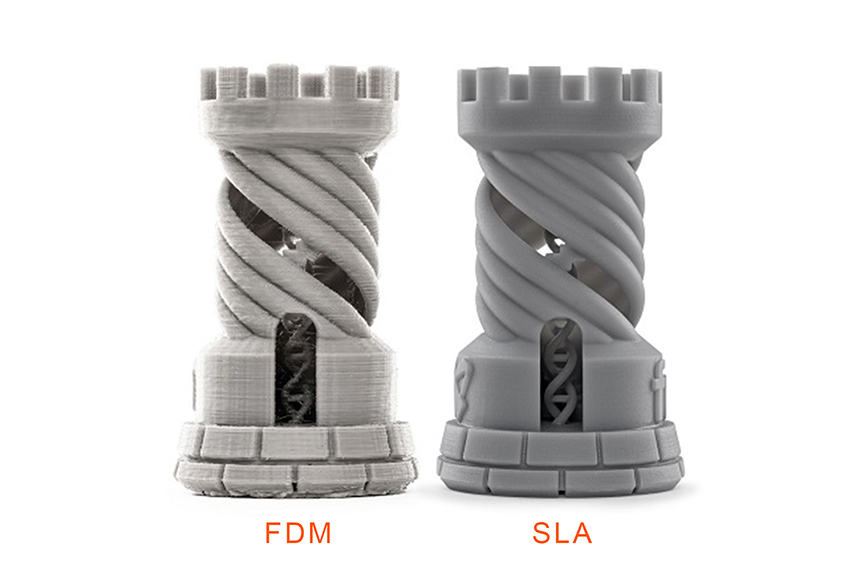
When comparing quality between 3D printer resin vs filament, the former is far much superior owing to a strong laser which can make small movements along the outlines of the model for very accurate dimensional precision. Some 3D printers for architects move up to 10 microns compared to the typical 50 to 100 microns of FDM printers. This produces detailed printed objects with extremely high resolution and intricate depth.
The high resolution of SLA printers is as a result of the small size of the optical spot of the laser focus or the projector’s pixels in DLP printing. Compared to FDM printing, SLA prints at a smaller minimum layer height which produces excellent detail and precision and less force is applied for a smoother surface. However, you can still get high quality with FDM printers which use nylon, PLA or PETG filaments as long as you don’t mind a longer printing time.
Besides the high resolution and details, the surface texture of SLA objects is also smoother because they undergo less amount of stress than in filament printing. Additionally, the high temperature used during FDM may produce print imperfections that would need post-processing to clear them.
The level of resolution in FDM printing will depend on the diameter of the nozzle as well as the extruder’s precision. The typical nozzle’s diameter is 0.4 mm which balances precision, speed and quality. Wider nozzles are available for fast printing and you can also get narrower ones with as small as 0.1 mm diameter for better precision and quality. However, the latter are also slower due to their small nozzles.
 Safety
SafetyDue to their nature, resins may produce chemical reactions and release toxic pollutants that may irritate our eyes, cause respiratory issues and worsen skin allergies with rashes and dermatitis. SLA 3D printers also use resin and UV light which can cause burns if it lands on skin that is then exposed to the sun. Improper disposal of resin could also be detrimental to aquatic life such as fish.
The risks of filaments are the harmful fumes emitted when melting filaments like ABS or nylon at high temperature. Inhaling these fumes which have Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) is harmful Trusted Source 3D Printers May Be Toxic To Humans www.forbes.com to our health.
Some precautions include using nitrile gloves to handle resin and wearing safety glasses for your eyes. Also, use an enclosed 3D printer and place it in a well-ventilated area during operation to limit your exposure to fumes and other irritants.
You can extrude more material to print thicker layers at a faster rate with filament printers whereas in resin 3D printing, each layer has a small surface area which increases printing time. Post-processing also takes longer in SLA because of the extra steps included. However, DLP which uses a light projector instead of a laser beam to print entire layers at a time is much faster than FDM. Masked Stereolithography Apparatus (MSLA) which uses UV curing light to achieve the same is also faster than filament printers.
You could also reduce FDM printing time with a wider nozzle with a higher flow rate although this might affect quality.
Between SLA 3D printer vs FDM, filament printing provides more options for materials and colors. Most of them work with ABS, PLA and PETG filaments as well as TPU, nylons, and PLA blends of metals, ceramics, wood and carbon fiber.
Although there are few premium FDM printers that use proprietary filaments, most of them use standard filament rolls available in diameters of 1.75 or 2.85mm.
Filament manufacturers avail them in a wide variety of colors, with some of them providing RAL colors upon request.
On the other hand, resin 3D printers are limited to proprietary resin materials. There also few color choices which include white, grey, black and clear resins. The advantage of SLA printing is the ability to create specialized prints that are flexible and heat-resistant for industrial uses.
 Adhesion
AdhesionFDM printing is prone to adhesion of excess plastic or supports in overhangs while
SLA 3D printed models usually have plenty of leftover resin, and probably supports.
We have already pointed out that the bulk of FDM printers use standard filament rolls. The filaments are inexpensive and since nozzles can last for a whole, are relatively cheap and some models include spares in the package, 3D printers are more budget-friendly than SLA printers.
What makes resin 3D printers high-maintenance is that you need to replace resin and the FEP film in the resin tank. You may also have to replace the resin tank itself if it is too smudged for the laser to project a precise image. These replacements are costly over time.
For both SLA 3D printer and FDM, users have to replace the build platform if it is impaired when you lift the printed model from its bed.
SLA 3D printers come with rubber gloves to remove the leftover resin and clean it using isopropyl alcohol. Besides that, you may have to cut off supports from the model and harden the piece after printing by curing it with UV light. This is why post-processing takes longer in SLA than in FDM printing.
FDM is much simpler because you only need to remove the extra plastic and any support. You can remove this with your fingers or a palette knife, and then sand to smoothen the surface. Some pieces are flexible and do not need supports for convenient removal of printed objects.
Use SLA for a model with amazing detail and a smooth texture. For instance, creating casting molds for mass production of items such as toys and jewelry.
Use FDP to create a strong, durable prototype in a short printing time. This type of 3D printing is ideal for hobbyists and DIY tasks at a low cost.
 Ease of use
Ease of useIf we factor in how long it takes to 3D print when using resin 3D printer vs filament, the latter wins in ease of use. Despite adhesion, you can easily lift and remove the final filament print from its bed with a palette knife, snip off the bits of excess plastic and then sand the surface.
Comparatively, SLA 3D prints are harder to remove because there is usually a lot of leftover resin. You will also need to wash off the resin with isopropyl alcohol. The whole process probably takes as long as post-processing in FDM.
Having said that, there is still a learning curve with every type of 3D printer because you need to level the bed, load the material properly and be familiar with the software.
Earlier while pitting resin 3D printer vs filament precision, we noted that nozzle size and extruder precision determine the print quality in FDM. The adhesion between layers is also another factor that will affect the end results.
So, how long does it take to 3D print? Bonding layers while printing filaments is a slow process which could cause shrinkage, misalignment or warping of layers as the upper layers squeeze the lower layers. It could also create zits and blobs which affect smoothness and precision of the prints. SLA printing wins for quality.
FDM is superior in strength, with filaments such as polycarbonate boasting of tensile strength of 9,800 psi. It is a go-to material for manufacturing industries because it is strong, durable and can withstand heavy-duty impact. Other robust filaments include carbon fiber, and nylon which has tensile strength of 7,000 psi compared to UV resin’s strength of 3,400 psi.
Flexible filaments like TPU also impart printed models with top-grade strength and resistance to wear and tear. Some premium SLA printers that use ABS-like resin produce strong models but resin prints are generally brittle in nature, compared to FDM.
If you are looking for a 3D printer that will extrude material at a high flow rate to reduce printing time and will not cost a fortune, then you should choose an FDM printer such as Creality Ender 3 V2. It has been upgraded with a silent motherboard for quiet operation, power voltage of 115V or 230V, onboard storage for accessories, and a knob for convenient feeding and changing of filaments. Otherwise, consider ANYCUBIC Photon Mono X which supports remote operation and has high printing speed of 60mm/h, a precise Z-axis and LCD-based SLA to produce high-quality prints. We hope that our in-depth review of the key features of 3D printer resin vs filament models as well as their respective pros and cons will help you to identify the right printer that will be most suitable for you.