
If you are on this page, it means you’ve gotten started in 3D printing, and we don’t have to bore you about all the ways that 3D printing has developed and can be useful. Trusted Source The past, present and future of 3-D printing - The Washington Post Although the technology is being used mostly for prototypes, its use is likely to grow as the usability and economics make more sense. www.washingtonpost.com However, it also means that you’re having some printing problems in the form of 3D printer filaments not feeding.
Luckily, this is a solvable problem. Though there might be many reasons (and corresponding solutions) for a printer not feeding filaments, we will be covering all bases to help you get back to printing again.
In the spirit of offering endless value, we would also be providing tips on how to avoid this problem and some other similar ones.
We have established that there is more than one reason for this problem, but all can be solved as well as prevented. Some of the issues are:
Each of these problems is touched on below:

Though this tube isn’t needed in all types of 3D printers, some Bowden-style printers (the Ender 3 model included) require this tubing to enhance the extrusion of their filaments.
Unfortunately, if this tubing is within the melting zone, it would soften and block the filament from being extruded. This is why it isn’t very uncommon to see ender 3 filaments not feeding. The problem is not permanent, though, and can be easily solved by replacing the PTFE tubing used in the lining with a new one. A smart choice recommended by experts and customers alike is the Authentic Capricorn PTFE Bowden Tubing.
For printing to go smoothly and as planned, the extrusion must be seamless and easy to control/pace. This is unlikely to be so if the extrusion path is blocked or clogged. Issues with the extrusion rate could completely damage the print even if it isn’t serious enough to stop the printing midway.
If you feel the faults with the feeding of the filament stems from here, you should check out the nozzle and the filament spool to be sure. The clogging may result from a too high or too low extrusion temperature. If there are no problems specifically wrong with the spool or nozzle, try changing the temperature after unclogging.
The retraction settings of a 3D printer allow users to control the distance and rate of retraction of the filament into the extruder’s nozzle. This is particularly important when the extrusion location is changing as printing goes on. A bad setting to this critical printing element could come in one of two ways.
As the name implies, the extruder motor is in charge of pushing the filament into place for the extrusion of softened (melted) filament to take place. If the extruder motor is weak, it will affect the feed rate and the extrusion rate. Most times, this might start to manifest initially as a clicking sound made by the extruder motor. If you have to change the motor, a quality option like the STEPPERONLINE Nema 17 Stepper Motor is a great choice.

Everyone knows how the tightness of the spring could affect the feeding of the filament, but very few people spend enough time perfecting the setting. You are going to need to get the hang of making this setting as perfect as possible if the goal is to 3D print homes Trusted Source The world's first 3D-printed neighborhood is being built in Mexico for families living on $3 a day - CNN A giant 3D printer built two houses in an impoverished, rural part of Mexico last week, breaking ground on what will be the first 3D-printed neighborhood in the world. amp.cnn.com , as has been reported by CNN.
There are also the drive gears to worry about. Like all mechanical parts of machines, they lose effectiveness over time, and worn-out gears are a common reason for the poor feeding of filaments. A change of drive gears and hot end are valid solutions to this problem.
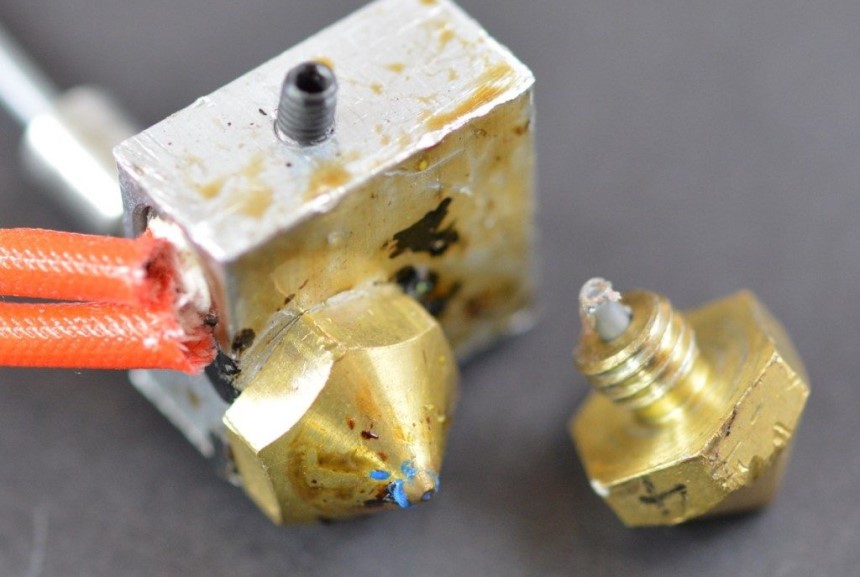

Another reason (and one of the most common) for the poor feeding of filament in 3D printers is a clogged nozzle. This isn’t something that can be prevented from happening but regularly cleaning the nozzle would keep the detrimental effects of this at bay. There are other reasons why filament could be sticking to the nozzle as well, and they should be considered if other solutions are being mooted.
It should be noted that a clogged nozzle could be partially or fully clogged. The particular one plaguing the effectiveness of your printer would be dependent on the extensiveness of stuck filament in the nozzle.
The extent of clogging would consequently influence the method that is applied in unclogging the nozzle. The methods for unblocking the nozzle are explained below.
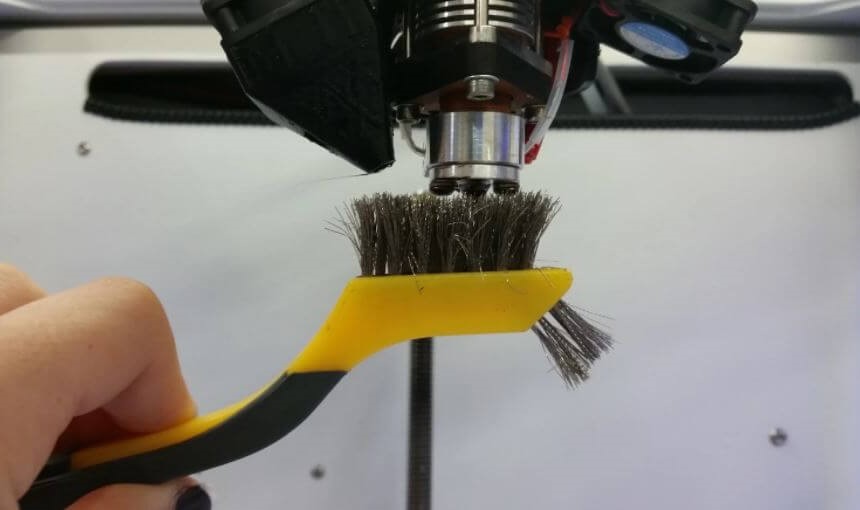

Use a wire brush. The commonly used option is a brass wire brush
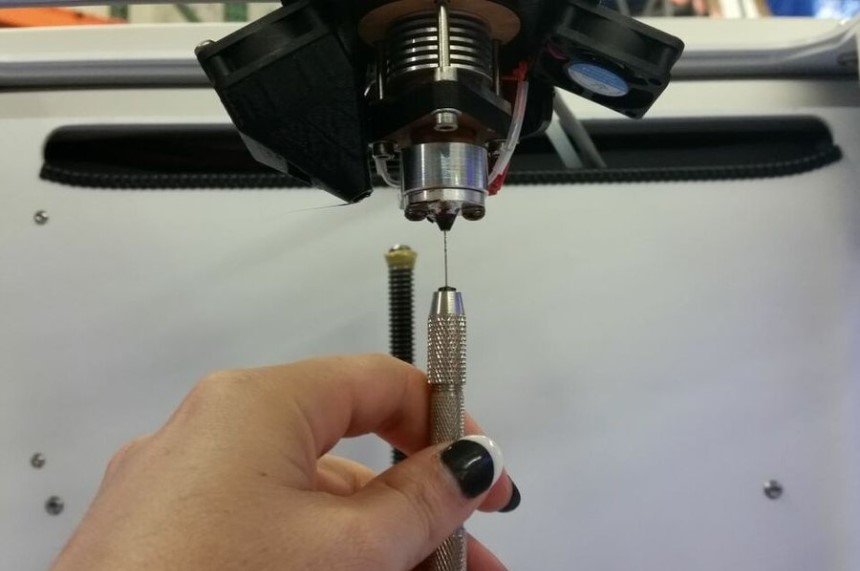

Use a guitar string or needle. The needle and string have a smaller diameter than the nozzle and are less likely to damage it. Similar to the manual pushing method for unblocking partially clogged nozzles, the nozzle is to be heated first before the needle or string is used. Subsequent extrusions should see the blocking particles released along with the extruded filaments.
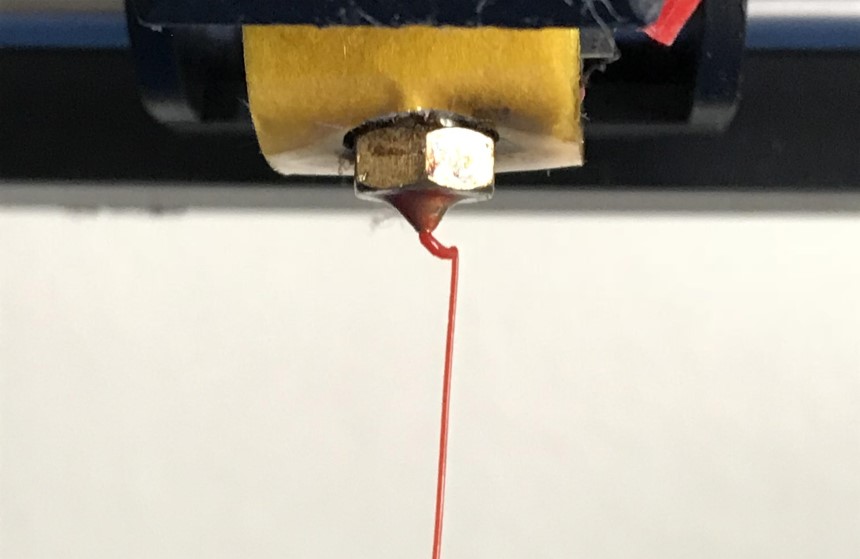
We have explained how to go about solving the problem of a clogged nozzle and have even given some solutions to the other potential problems but before resorting to those, here are quick and specific ways to go about fixing the filament feeding in your printer:
You might find yourself in a unique situation where many of the solutions we have offered would not work out for you. One problem that could have occurred if your printer is an Ender 3 would be that of a loose extruder cog. Simply lining the cog up with the feeder disc and retightening it would solve the problem.
As we have stated earlier, leftover filaments may harden in the nozzle during extrusion and printing and gradually build up a significant obstruction. This type of obstruction could slow down the plastic flow and facilitate the buildup of an even bigger clog. This can be solved by regular cleaning and maintenance of the extruder and nozzle.
Before printing, the extruder has to be primed. This might even be more critical if a different plastic material was used in the previous cycle. Printing plastics have different characteristics (for instance, PETG differs from ABS) and priming (and) ensures that the factors from a previous cycle do not affect the current one.
This is a problem that originates from the hot end, filament, and poor heat settings. As the name implies, the heat creeps us and raises the temperature of the hot end prematurely, causing the filament to melt early as well.
The problem could develop during or after printing and manifest in a finished print as a fuzzy top. The issue of heat creep comes up in hot ends without a PTFE liner. Hence, the PTFE liner mentioned earlier (which can influence poor filament feeding when of low quality) is not simply a design prop. Thankfully though, the heat creep is solved by:
3D printing is interesting enough without the developments it always seems to be undergoing. However, it would be difficult to enjoy if you keep on stumbling from problem to problem, and we are here to help you solve the problems and maintain your momentum.
That aside, though, you shouldn’t feel too badly about stumbling onto this issue as it is one that only experience can guide against. The problem of a 3D printer filament not feeding is that popular, and we hope to have helped solve yours.
Regardless of whether you solve this problem on your own, don’t give in to these growing pains and keep printing! If we haven’t, it might be time for you to call an expert. Besides repair, another benefit of inviting an expert is that you get to learn more and ask the questions that might have been bugging you.





